- Route calls over the Internet,
- Integrate with software tools,
- And enable employees to communicate from anywhere using IP phones, softphones, or mobile apps.
Key Takeaways
|
What is VoIP & How Does it Work?
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is a technology that lets you make phone calls using the internet instead of a traditional phone line. VoIP works by converting analog voice signals into digital data packets. You speak into a microphone or phone. The device converts your voice from analog to digital using a codec (short for “coder-decoder”). The digital signal is split into small data packets. Each packet includes part of the conversation and information about where it should go. These packets travel over the Internet to the other person's device. The receiving device assembles the packets in the correct order and converts them from digital to sound. The entire process happens in milliseconds, so the conversation feels natural.Types of VoIP Services
VoIP services are divided into two main types: hosted VoIP and on-premises VoIP.-
Hosted VoIP (Cloud-Based)
-
On-Premise VoIP (Self-Hosted)
Business Requirements for VoIP Setup
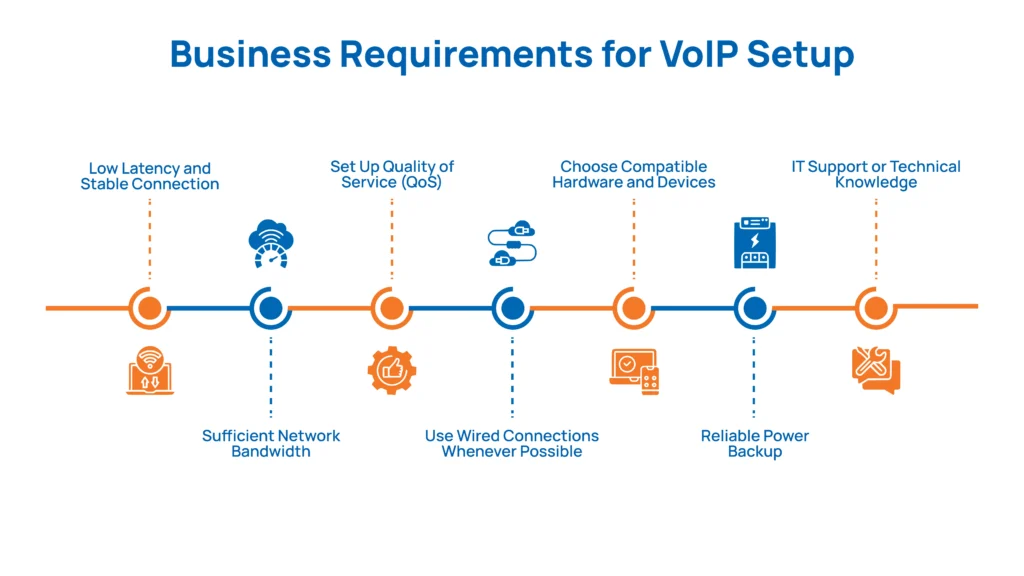 VoIP needs a strong, stable internet connection to deliver clear, uninterrupted calls. Effective VoIP planning ensures your network, hardware, and team are fully prepared for a smooth and reliable communication system rollout. Here are the essential requirements you should check and prepare:
VoIP needs a strong, stable internet connection to deliver clear, uninterrupted calls. Effective VoIP planning ensures your network, hardware, and team are fully prepared for a smooth and reliable communication system rollout. Here are the essential requirements you should check and prepare:
-
Low Latency and Stable Connection
-
Sufficient Network Bandwidth
-
Set Up Quality of Service (QoS)
-
Use Wired Connections Whenever Possible
-
Choose Compatible Hardware and Devices
- VoIP-enabled phones or headsets.
- A router that allows QoS configuration.
- A modem that can handle your bandwidth needs.
- (Optional) Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs) are available if you plan to use traditional phones.
-
Reliable Power Backup
-
IT Support or Technical Knowledge
How to Set Up a VoIP Phone System That Scales With Your Business
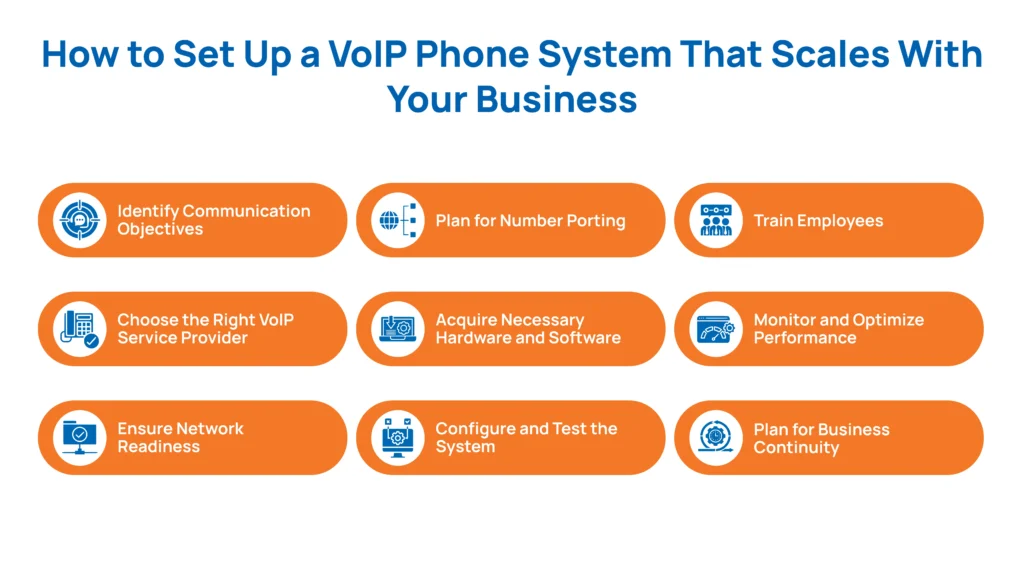 Below is how to set up a VoIP phone system that meets your current needs and effortlessly scales as your business grows.
Below is how to set up a VoIP phone system that meets your current needs and effortlessly scales as your business grows.
-
Identify Communication Objectives
| Feature | Description |
| Auto-Attendant | Automated call routing to appropriate departments or individuals. |
| Voicemail-to-Email | Receiving voicemail messages directly in your email inbox. |
| Call Recording | Recording calls for quality assurance or compliance purposes. |
| Mobile Integration | Accessing the VoIP system via mobile devices for remote work flexibility. |
-
Choose the Right VoIP Service Provider
-
Ensure Network Readiness
- G.711: Approximately 80–90 Kbps per call (high-quality audio)
- G.729: Approximately 30–40 Kbps per call (compressed audio)
- G.722: Approximately 50–80 Kbps per call (HD voice)
-
Plan for Number Porting
-
Acquire Necessary Hardware and Software
-
IP Phones
-
Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
-
Softphones
-
Configure and Test the System
 Connect IP phones directly to your network using Ethernet cables. Ensure each device receives a valid IP address through Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or static assignment. If you use analog phones, connect them to ATAs, which interface with your network to facilitate VoIP communication.
Configure routers and switches to support VoIP traffic. Implement Virtual LANs (VLANs) to segregate voice traffic from data, enhancing quality and security. Install and configure any necessary software.
VoIP software or softphone applications on user devices, ensuring compatibility with your chosen VoIP service provider. Adjust firewall settings to allow VoIP traffic on ports such as 5060 for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). Ensure security measures are in place to protect against unauthorized access.
Before full deployment, conduct pilot testing to evaluate system performance. Place internal and external calls to assess audio clarity, connection stability, and feature functionality.
Monitor crucial indicators such as latency (delay in voice transmission), jitter (variability in packet arrival), and packet loss. Acceptable thresholds are:
Connect IP phones directly to your network using Ethernet cables. Ensure each device receives a valid IP address through Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or static assignment. If you use analog phones, connect them to ATAs, which interface with your network to facilitate VoIP communication.
Configure routers and switches to support VoIP traffic. Implement Virtual LANs (VLANs) to segregate voice traffic from data, enhancing quality and security. Install and configure any necessary software.
VoIP software or softphone applications on user devices, ensuring compatibility with your chosen VoIP service provider. Adjust firewall settings to allow VoIP traffic on ports such as 5060 for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). Ensure security measures are in place to protect against unauthorized access.
Before full deployment, conduct pilot testing to evaluate system performance. Place internal and external calls to assess audio clarity, connection stability, and feature functionality.
Monitor crucial indicators such as latency (delay in voice transmission), jitter (variability in packet arrival), and packet loss. Acceptable thresholds are:
| VoIP Quality Metric | Acceptable Threshold |
| Latency | Less than 150 milliseconds |
| Jitter | Less than 30 milliseconds |
| Packet Loss | Less than 1% |
-
Train Employees
-
Monitor and Optimize Performance
-
Plan for Business Continuity
Top 4 VoIP Mistakes Businesses Make
 Implementing a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system can enhance communication efficiency and reduce business costs. However, inevitable mistakes can hinder its effectiveness. Here are a few best practices to ensure a smooth transition and optimal performance.
Implementing a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system can enhance communication efficiency and reduce business costs. However, inevitable mistakes can hinder its effectiveness. Here are a few best practices to ensure a smooth transition and optimal performance.
-
Overlooking Bandwidth Requirements
-
Neglecting Employee Training
-
Underestimating Security Needs
-
Skipping Pre-Deployment Testing
Streamline Customer Engagement with PerfectSoft.AI’s Intelligent VoIP Solutions
 At PerfectSoft.AI, we deliver intelligent, high-performance contact center solutions to improve customer satisfaction, boost agent productivity, and streamline operations.
Whether you manage a large-scale BPO, a customer service department, or an outbound sales team, our technology helps you stay connected across all channels while ensuring crystal-clear
We provide advanced VoIP-based Telecom Voice Services that guarantee:
At PerfectSoft.AI, we deliver intelligent, high-performance contact center solutions to improve customer satisfaction, boost agent productivity, and streamline operations.
Whether you manage a large-scale BPO, a customer service department, or an outbound sales team, our technology helps you stay connected across all channels while ensuring crystal-clear
We provide advanced VoIP-based Telecom Voice Services that guarantee:
- High-Quality Voice Calls – Clear and uninterrupted voice communication.
- Reliable Connectivity – Stable and secure connections across all regions.
- Global Reach – Seamless communication with teams and customers worldwide.


Comments