Understanding PBX: How it Works
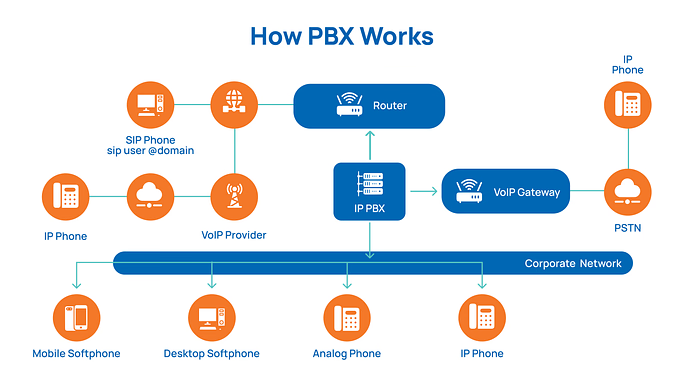 PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange. A telephone system is used within a business or organization to manage both incoming and outgoing calls, as well as internal communication between employees. PBX systems are installed on-site and use dedicated hardware to operate.
PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange. A telephone system is used within a business or organization to manage both incoming and outgoing calls, as well as internal communication between employees. PBX systems are installed on-site and use dedicated hardware to operate.
- A PBX system connects internal phone lines within a company to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) for external calls.
- It uses physical infrastructure, such as copper phone lines or digital T1 connections.
- Calls are routed through this system using on-premises equipment such as switches, servers, and desk phones.
Read More: How to Manage Multiple PBX VoIP Service Providers
Types of PBX Systems
| Type | Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who Uses PBX and Why
PBX systems are best suited for organizations that operate from a fixed location and have the resources to maintain on-site equipment. Businesses with an in-house IT team, stable infrastructure, and specific security or compliance requirements may prefer PBX for its control and reliability. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and legal services, where data privacy and consistent communication are crucial, often rely on PBX systems. They’re also a preferred choice for companies that do not require remote work capabilities or have limited dependence on cloud services.Understanding VoIP: How it Works
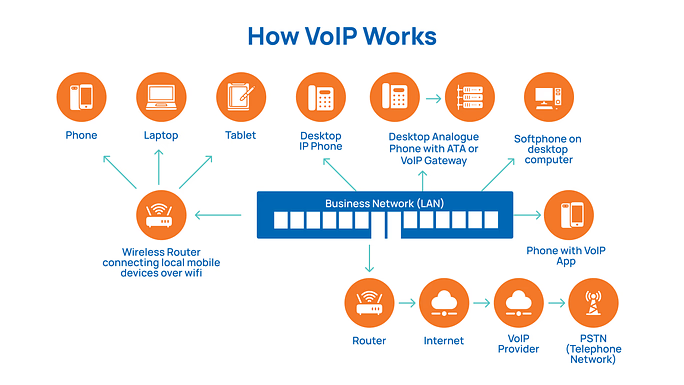 VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is a modern phone system that allows voice calls to be made using an internet connection instead of traditional phone lines. VoIP is widely used in both business and personal communication due to its flexibility, lower costs, and advanced features.
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is a modern phone system that allows voice calls to be made using an internet connection instead of traditional phone lines. VoIP is widely used in both business and personal communication due to its flexibility, lower costs, and advanced features.
- VoIP works by converting voice signals into digital data.
- These data packets are transmitted over IP (Internet Protocol) networks, a business’s internet connection. Once the packets reach the recipient, they are converted back into audio.
- This process allows users to make and receive calls using various devices, including computers, smartphones, VoIP-enabled desk phones, and tablets. VoIP systems often include additional communication tools, such as video conferencing, messaging, and file sharing.
Common Types of VoIP
| Type | Description |
| Hosted VoIP (Cloud-Based) |
|
| On-Premise VoIP |
|
Who Uses VoIP and Why
VoIP is widely used by startups, small to mid-sized businesses, and remote or hybrid teams that need a flexible and scalable communication solution. It’s also a strong choice for organizations that want to reduce phone system costs or integrate calling with other digital tools like CRMs, help desks, or collaboration platforms. Because VoIP supports calling from virtually anywhere with an internet connection, it's beneficial for businesses with mobile workforces or multiple office locations. Its ability to grow with the company and support advanced features makes it a preferred option in today's digital-first work environments.PBX vs. VoIP: Understanding the Key Differences
Choosing between VoIP and PBX can significantly impact your business communication. Here’s a breakdown of how these systems differ and what each offers.-
Feature Comparison: PBX vs. VoIP
PBX Phone System Features
Premise-based PBX systems provide the core functionality needed for office communication. These features are generally accessed via desk phones, and their scope is limited compared to modern VoIP systems. Here is a list of standard PBX features:- Voice Calling: Basic outbound and inbound calling capabilities.
- Call Transfer: Allows internal routing of calls between extensions.
- Call Hold / Call Waiting: Lets users pause and switch between calls.
- Voicemail: Basic message storage accessible from the desk phone.
- Caller ID: Displays the incoming caller’s number.
- Faxing: Supports analog fax machines.
- Audio Conferencing: Enables multi-party voice calls.
- Call blocking: Restricts incoming calls from specific numbers.
VoIP System Features
VoIP solutions are built to support modern communication workflows. They include a broader range of features, many of which are cloud-based and accessible from various devices, including PCs, mobile phones, and tablets. Below are the voice and call management features- IVR (Interactive Voice Response) and ACD (Automatic Call Distribution): These systems automatically direct callers to the correct department or agent.
- Call Forwarding: Routes calls to multiple numbers or devices until answered.
- Voicemail Transcription: Converts voice messages into text and delivers them via email or app.
- Automated Dialing Modes: Includes power, predictive, and preview dialing for outbound teams.
- Call Parking, Call Flip, Hot Desking: Lets users switch devices mid-call or share phones among users.
- Call Queuing and Automated Callbacks: Organizes incoming calls during high-volume periods.
- Advanced Call Routing: Routes based on agent skills, availability, time, or custom rules.
- Call Recording and Transcription: Automatically logs and transcribes calls for review or training.
- Call Monitoring Tools: Features like whisper, barge, and listen-in for live supervision.
Scalability and Flexibility: PBX vs. VoIP
A phone system should grow with your business. Here's how PBX and VoIP compare in these areas.PBX: Limited Scalability and Low Flexibility
Expanding a PBX system requires physical infrastructure upgrades. Technicians will need to install additional phone lines and hardware, which is time-consuming and costly. Your location or building capacity may restrict the number of available lines. There is no option for dynamic, on-the-go changes; scaling is limited and rigid. PBX systems are tied to specific office locations and desk phones. Employees can’t access the system remotely or from mobile devices. Adding a new area means setting up an entirely separate PBX installation. There's little to no integration with cloud-based or mobile-first tools.VoIP: High Scalability and Maximum Flexibility
Scaling with VoIP is quick and easy; just add new users in the admin dashboard. Most providers allow user additions in real time without needing hardware changes. Upgrades usually involve switching to a higher-tier plan, often within minutes. No cabling, no technician visits, and minimal setup disruption. With a single platform, VoIP systems can handle growth across teams and office locations. VoIP works on multiple devices: desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. Your team can make and receive calls from anywhere with an internet connection. Real-time syncing ensures consistent communication across all devices. VoIP supports mobile apps and browser-based calling, ideal for hybrid and remote teamsg. It easily integrates with other tools like CRM software, email platforms, and team chat apps.Call Quality and Reliability: PBX vs. VoIP
PBX and VoIP offer solid performance, but they differ in delivering and maintaining call quality, especially under varying network or infrastructure conditions. Here is how they differ:PBX: Stable and Dependable
PBX systems are generally known for their reliability. Because they run on the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) using physical copper wiring, they’re less affected by bandwidth issues or network congestion. Outages are rare, and if supported by standard backup systems, the system tends to remain functional even during power interruptions. Regarding call quality, PBX systems provide consistent audio performance but aren’t entirely immune to issues. Problems like echo, line noise, or dropped calls can still occur, particularly during severe weather or due to aging infrastructure. However, since these systems don’t depend on internet connectivity, they maintain steady performance in most office environments.VoIP: Clearer Audio, Internet-Dependent
VoIP systems often deliver higher call clarity, thanks to HD voice technology and modern compression algorithms. Many platforms also include advanced features like noise suppression and background noise cancellation, which help improve audio quality, especially in busy or remote work environments. However, VoIP reliability depends entirely on the strength and stability of your internet connection. Users may experience jitter, lag, or dropped calls if the connection is slow or unstable. To maintain a reliable VoIP experience, businesses should ensure a minimum of 100 kbps of bandwidth per call and consider having backup power sources or failover connections.Read More: How Much Bandwidth Does VoIP Use?
Hardware, Installation, and Setup: PBX vs. VoIP
Here’s how PBX and VoIP differ in terms of equipment and setup.PBX: Hardware-Heavy and Complex Installation
A PBX system requires a range of physical components to function. This includes desk phones for each user, structured cabling, modems, splitters, wall jacks, and on-site PBX servers. Many businesses also install backup power systems to ensure continuous service during outages. Installing a PBX system is a time-consuming process. It involves coordinating wiring, equipment setup, and configuration with technicians. Depending on the size of the office and the number of users, installation can take anywhere from several days to several weeks. Due to its complexity, it also requires IT support for maintenance and future updates.VoIP: Minimal Equipment and Fast Setup
VoIP systems require less hardware. An internet connection, a router, and compatible devices, such as computers or smartphones, are needed to get started. For businesses using phones, adapters such as an ATA or a VoIP gateway can connect those phones to the internet. Optional hardware may include IP phones, headsets, or speakerphones, but these are not required for the system to function. Installation is simple and can often be completed in a single day. Most VoIP platforms are cloud-based, which means setup is handled through an online portal. However, initial user training is essential because VoIP systems offer a wide range of features. Teams may need time to learn how to configure call flows, set up greetings, use mobile apps, and take advantage of advanced calling features. Choosing a provider that offers customer support and training resources can help speed up the adoption process.Security: PBX vs. VoIP
PBX and VoIP offer secure options, but their approaches to managing and handling threats differ due to the technologies they rely on.PBX: Physical Control, Lower Risk of Cyber Threats
PBX systems are more secure by design because they operate within a closed, physical network. Since they use landlines and are not connected to the internet, they are less exposed to external cyber threats, such as hacking, data breaches, or DDoS attacks. However, PBX systems are not entirely risk-free. Physical security becomes essential; access to the equipment, server rooms, and internal wiring must be restricted. Any unauthorized access to this hardware can compromise the system. Also, internal misuse or toll fraud (unauthorized long-distance calls) can occur if strict access controls aren’t in place.VoIP: Internet-Based with Greater Risk, But Strong Protections Available
VoIP systems run over the internet, which opens the door to potential cyber threats, including call interception, phishing, and service disruptions. Because of this, VoIP systems require strong digital security measures to protect voice data and user privacy. Many VoIP providers include security features like encryption (e.g., TLS and SRTP), firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication. Businesses can also implement VPNs and regularly update software to reduce vulnerabilities. While VoIP may increase exposure to online threats, these risks can be effectively managed with proper configurations and security protocols in place.Cost Comparison: PBX vs. VoIP
Setting up a PBX means purchasing physical hardware, such as servers, routers, gateways, and desk phones. Beyond the hardware, businesses must also factor in installation and setup costs, often involving hiring technicians. These initial costs can add up quickly, especially for companies setting up in multiple locations or expanding their team. There are recurring costs such as software licensing fees, system maintenance, and traditional phone line charges. VoIP, on the other hand, offers a more budget-friendly approach. The initial setup cost is low, often limited to purchasing IP phones, and many businesses can use their existing computers and mobile devices. Monthly VoIP plans can range from $20 to $50 per user. Many providers offer volume discounts or lower pricing for annual commitments. While some providers provide certain features as add-ons, most advanced tools are bundled into higher-tier plans that remain cost-effective. Additionally, VoIP providers handle system maintenance, reducing the need for in-house IT support and keeping long-term expenses predictable.PBX vs VoIP: A Detailed Comparison
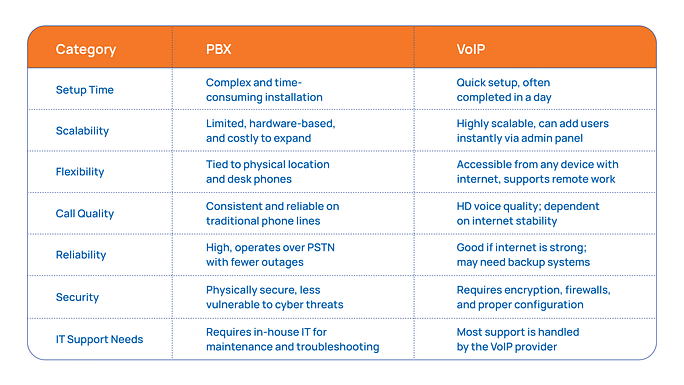
PBX vs. VoIP: Which Phone Systems is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between PBX and VoIP depends on your business’s specific needs. Here’s a breakdown of the essential factors to consider when making your decision.-
Budget
-
Business Size
-
IT Capabilities
-
Growth Plans
-
Remote Work Needs
Migration Challenges: Smart Tips for a Smooth Transition to VoIP
Switching from a PBX system to VoIP can feel like a big step, but it doesn't have to be a painful process. With the proper planning, your transition can be smooth, quick, and disruption-free.- Start by auditing your current phone setup: What features do you use? What hardware is still working? Who needs access to the system?
- Then, choose a VoIP provider that supports your must-have features, offers migration support, and has a proven track record of delivering high-quality service. For example, PerfectSoft.AI’s Telecom Voice Services offer secure, high-quality VoIP with advanced capabilities and global reach.
- To avoid call drops or poor quality, make sure your internet bandwidth can handle concurrent calls; about 100 kbps per call is a safe benchmark. Have a backup internet connection or power source in place, especially for high-volume teams.
- Train your staff early. VoIP systems offer advanced features, but your team needs to know how to use them to benefit from them fully. A short investment in onboarding pays off in faster adoption and fewer support tickets later.
Enhance Connectivity and Drive Scalable Growth with PerfectSoft.AI’s Advanced VoIP Solutions
 At PerfectSoft.AI, we create seamless, intelligent, high-performance contact center solutions to enhance customer satisfaction, agent engagement, and operational efficiency. Whether running a high-volume BPO, customer service team, or sales operation, our solutions empower you to connect across all channels while maintaining crystal-clear voice communication.
Our Solutions Include:
Telecom Voice Services – Ensure high-quality, secure, and reliable voice connections, advanced VoIP, and global reach.
Why Choose PerfectSoft.AI?
At PerfectSoft.AI, we create seamless, intelligent, high-performance contact center solutions to enhance customer satisfaction, agent engagement, and operational efficiency. Whether running a high-volume BPO, customer service team, or sales operation, our solutions empower you to connect across all channels while maintaining crystal-clear voice communication.
Our Solutions Include:
Telecom Voice Services – Ensure high-quality, secure, and reliable voice connections, advanced VoIP, and global reach.
Why Choose PerfectSoft.AI?
- Seamless Integration: Connect with your existing CRM and business tools.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Optimize operations without breaking the bank.
- Scalability & Flexibility – Easily scale your contact center operations.
- 24/7 Support: Get personalized, round-the-clock assistance whenever you need it.


Comments